In this section we will disscuss about another methord of creating a table. Let see how to create a table with the use of subquery but before this we will see the meaning of subquery
Subquery:
“SQL statement embedded inside a another SQL statement is called a subquery “
Syntax:
CREATE TABLE Table_name (column1,column2,…..,column N)
AS subquery
In this syntax create table specify that creation of new table,Table_name specify the name of the table,column1, ….,column N etc specify the columns name of the table, AS is a keyword which states that we are going to create a new table from a exiting table,In subquery we can write the SQL select statement to select the rows from the other table.
Example:
create a table employees2 from the exiting employees
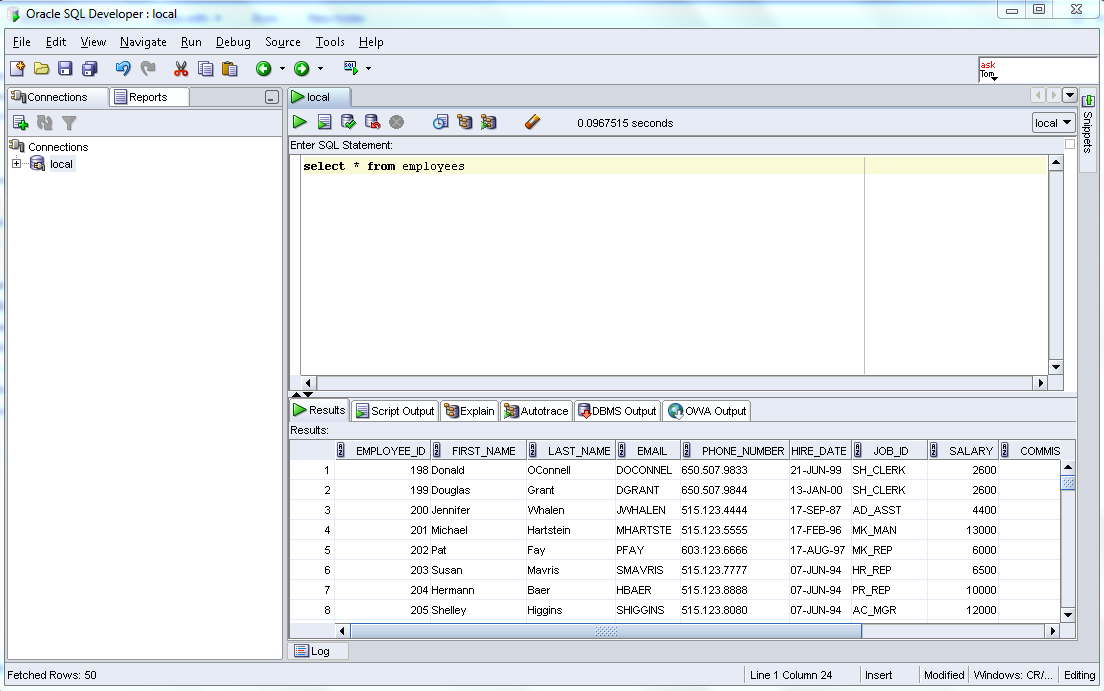
CREATE TABLE EMPLOYEES2 (ID,FIRST_NAME,LAST_NAME,SALARY,DEPT_ID)
AS
SELECT EMPLOYEE_ID,FIRST_NAME,LAST_NAME,SALARY,DEPARTMENT_ID
FROM EMPLOYEES
Note : The above statement create a employees2 with the same structure and along with data of employees table.
I am interested in hearing your feedback, so that I can improve my articles and learning resources for you.connect with us on facebook, twitter
Subquery:
“SQL statement embedded inside a another SQL statement is called a subquery “
Syntax:
CREATE TABLE Table_name (column1,column2,…..,column N)
AS subquery
In this syntax create table specify that creation of new table,Table_name specify the name of the table,column1, ….,column N etc specify the columns name of the table, AS is a keyword which states that we are going to create a new table from a exiting table,In subquery we can write the SQL select statement to select the rows from the other table.
Example:
create a table employees2 from the exiting employees
CREATE TABLE EMPLOYEES2 (ID,FIRST_NAME,LAST_NAME,SALARY,DEPT_ID)
AS
SELECT EMPLOYEE_ID,FIRST_NAME,LAST_NAME,SALARY,DEPARTMENT_ID
FROM EMPLOYEES
Note : The above statement create a employees2 with the same structure and along with data of employees table.
I am interested in hearing your feedback, so that I can improve my articles and learning resources for you.connect with us on facebook, twitter